Today's highlights:
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
OpenAI Launches 'Deep Research' for ChatGPT to Streamline Complex Online Information Gathering
• OpenAI has launched a new ChatGPT feature called "deep research," designed to conduct complex online research and synthesize information efficiently
• This feature significantly reduces research time, completing tasks that would take humans hours in mere minutes, available for Pro users initially
• Deep research uses the advanced OpenAI o3 model to perform thorough web searches, analysis, and synthesis, marking a notable step towards AI's capability in generating new knowledge.
SoftBank and OpenAI Partner in $3 Billion AI Venture to Transform Businesses
• Japan's SoftBank Group and US-based OpenAI announce a joint venture to deliver advanced AI solutions, formalizing a memorandum of understanding setting up a 50-50 partnership
• SoftBank commits to a $3 billion annual investment for deploying OpenAI's AI technologies across its group companies, focusing on customized AI support for various business systems
• The collaboration aims to create AI agents tailored for Japanese enterprises, while also contributing to global AI infrastructure as part of the broader Stargate initiative in the US;
⚖️ AI Ethics
EU AI Act Launches, Enforces Tough Restrictions and Fines for Non-compliance
• The EU AI Act took effect in August 2024, introducing the world's first comprehensive regulatory framework for artificial intelligence, establishing strict rules and significant penalties for violations;
• The AI Act’s provisions on AI literacy and prohibited AI uses are now applicable:
Article 4: Providers and deployers of AI systems shall take measures to ensure, to their best extent, a sufficient level of AI literacy of their staff and other persons dealing with the operation and use of AI systems on their behalf, taking into account their technical knowledge, experience, education and training and the context the AI systems are to be used in, and considering the persons or groups of persons on whom the AI systems are to be used.
Article 5 of the EU AI Act prohibits certain AI practices that pose significant risks to individuals and society. These include AI systems using subliminal or manipulative techniques that impair decision-making, exploit vulnerabilities based on age, disability, or economic status, and conduct social scoring that results in unjustified discrimination. Additionally, AI systems for predictive criminal risk assessment based solely on profiling, unauthorized facial recognition databases, and emotion inference in workplaces or educational institutions are banned. Biometric categorization for sensitive attributes such as race, political views, or sexual orientation is also prohibited. The use of real-time remote biometric identification in public spaces is strictly limited to law enforcement under exceptional circumstances, such as preventing imminent threats or locating suspects, and requires prior authorization, fundamental rights impact assessments, and compliance with national regulations. Member States must ensure strict oversight, including annual reporting to the European Commission, while maintaining the option to impose stricter national laws.
• Non-compliance with the EU AI Act could cost companies fines up to 35 million euros or 7% of global annual revenue, surpassing penalties outlined in the GDPR for privacy violations;
Mark Zuckerberg Discusses Meta's Policy Changes and Future AI Initiatives with Employees
• At a Meta meeting, CEO Mark Zuckerberg defended policy changes loosening speech restrictions and ending diversity efforts, aligning with the Trump administration for improved government relations;
• Employees expressed dissatisfaction over internal changes like removing tampons from men's bathrooms, protesting by organizing sanitary product donations after recent Meta policies on diversity and inclusion;
• Zuckerberg addressed Meta's competition with TikTok and AI advancements, emphasizing large investments in data centers for AI, while noting DeepSeek’s open-source AI benefits for the company.
Taiwan Bans Use of China's DeepSeek AI Over National Security Concerns
• Taiwan has banned DeepSeek AI for governmental use, citing security concerns related to cross-border data risks and potential information leaks from the Chinese-developed technology;
• DeepSeek's open-source AI, praised for its advanced reasoning and cost-effective development, now faces global scrutiny over data privacy, leading to bans and warnings from several governments;
• US congressional offices have been advised against using DeepSeek, with ongoing reviews highlighting significant concerns regarding data security and the potential influence of foreign entities.
Proposed US Law Targets Chinese AI Investments and Research Collaborations with Severe Penalties
• A proposed US law threatens 20-year jail terms or $1 million fines for Americans downloading Chinese AI models or investing in related firms
• US companies face up to $100 million fines if caught transferring AI tech to China, as Congress pushes to block AI collaborations
• The UK's proposed law could impose five-year prison sentences for creating or sharing AI models that generate child sexual abuse material;
Sam Altman says OpenAI is ‘on the wrong side of history’ and needs a new open-source strategy after DeepSeek R1 shock.
• OpenAI executives, including CEO Sam Altman, discussed AI competition and open source strategy during a Reddit AMA amid challenges from Chinese firms like DeepSeek and U.S. regulations
• OpenAI considers open sourcing older AI models while acknowledging past missteps in its closed-source approach, but it remains a lower priority within the company
• OpenAI aims to reduce ChatGPT pricing despite losses on premium plans, while advancing its new Stargate data center project to boost AI performance;
🎓AI Academia
Acceleration AI Ethics Explored Through TELUS's Generative Language Tool Case Study
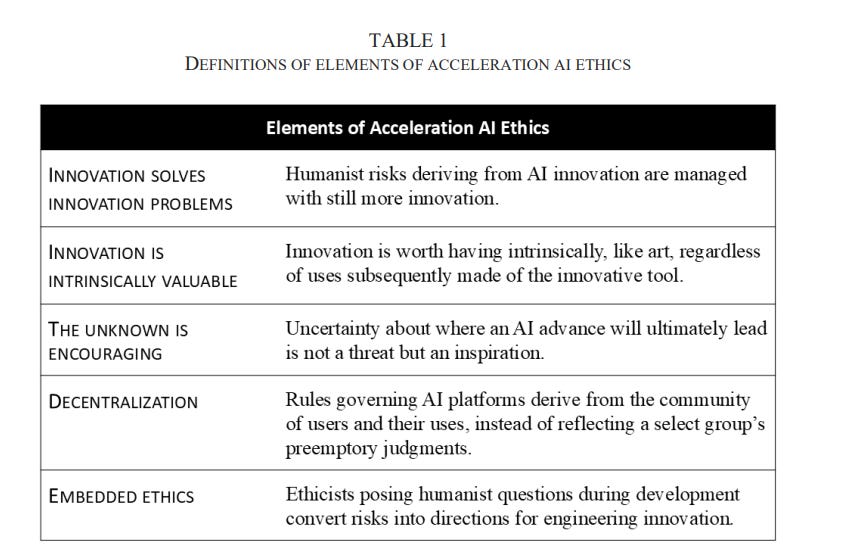
• The concept of acceleration ethics highlights using innovation to tackle AI-related risks, proposing that further innovation can effectively address challenges while maintaining intrinsic value and decentralized governance;
• The TELUS GenAI Conversational Agent serves as a case study for acceleration ethics, demonstrating how generative AI can balance social responsibility and innovation in real-world applications;
• This exploration of the TELUS use-case suggests that acceleration ethics could maximize social responsibility by integrating ethical considerations into rapid technological advancements.
Market-Based AI Governance Promises to Enhance Responsible Development and Risk Management
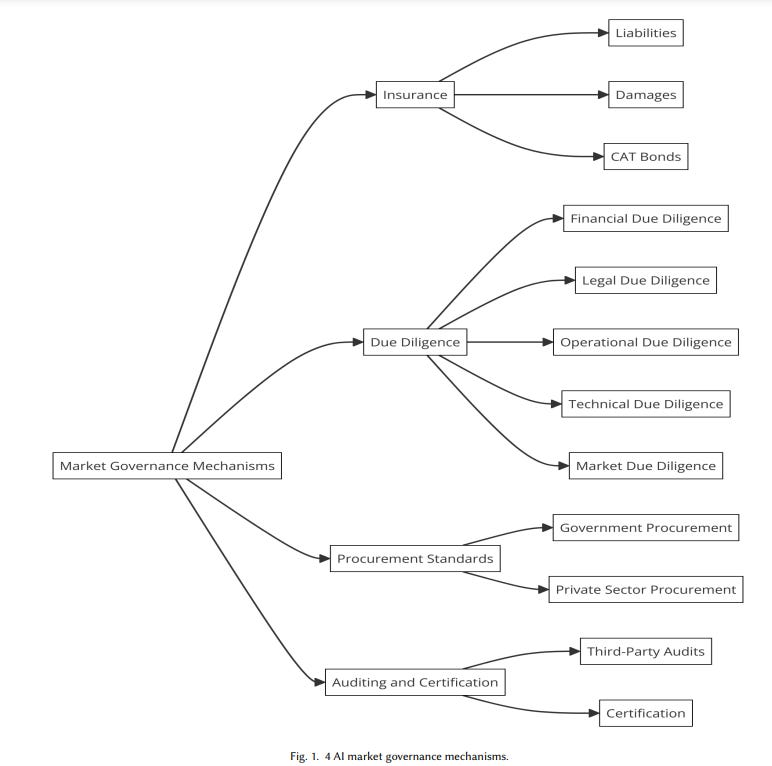
• A recent paper advocates for integrating market governance mechanisms like insurance, auditing, procurement, and due diligence into AI governance to complement traditional regulatory frameworks;
• The research highlights that market-based mechanisms can align AI risk with financial risk, potentially improving capital allocation and encouraging safer, accountable AI development;
• Researchers underscore that standardized AI disclosures, coupled with market incentives, could play a crucial role in promoting responsible AI practices by mitigating information asymmetries.
Open-Source Tool Enhances AI Ethics Implementation in Software Development Practices
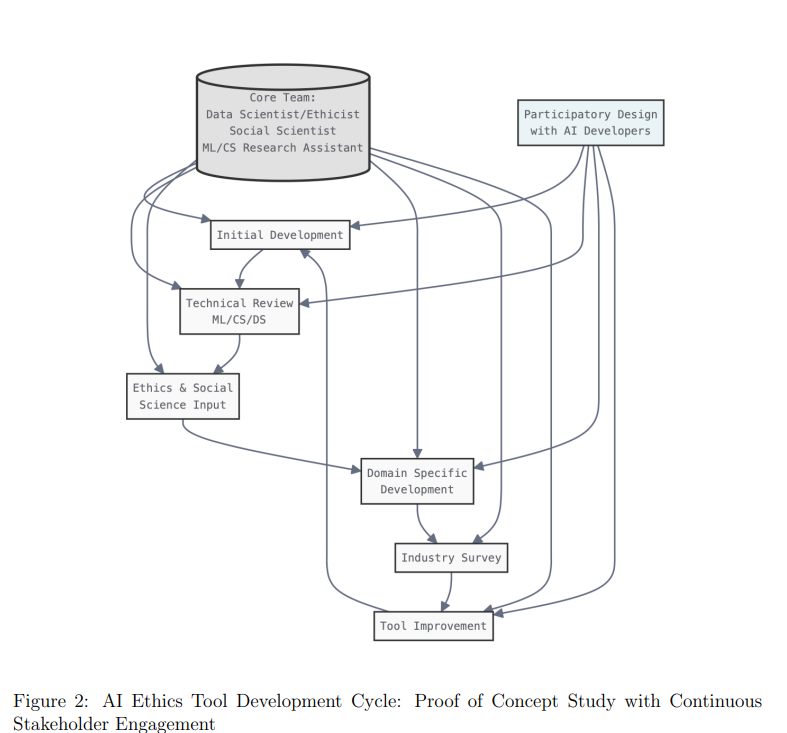
• An open-source tool has been developed to address the gap between AI ethics theory and practice by providing actionable guidance integrated into software workflows
• The tool is informed by normative ethical frameworks and validated in the U.S. autonomous driving industry through a proof of concept study
• Barriers like complex language and vague guidelines have hindered AI ethics adoption, but participatory design with industry practitioners promises improved accessibility.
Ethical Principles and Practices for Generative AI by Product Managers Explored
• A recent publication from leading universities explores the convergence of ethical principles and practical applications in responsible generative AI use by product managers;
• The study emphasizes the critical need for product managers to integrate ethical considerations into AI development processes, highlighting potential societal impacts;
• Researchers from prominent institutions advocate for more robust frameworks to ensure accountability and transparency in the deployment of generative AI technologies by companies.
Study Explores Decision-Making Complexities in Responsible Software Engineering for AI Development
• A study highlights the gap between ethical guidelines and their real-world implementation in AI software engineering, emphasizing the need for practical operational frameworks
• Research shows that interdisciplinary collaboration and a strong organizational culture of ethics are crucial for effective responsible AI software engineering
• Study underscores the complexity of embedding ethical principles in AI, due to conflicting priorities between software quality and business revenue objectives.
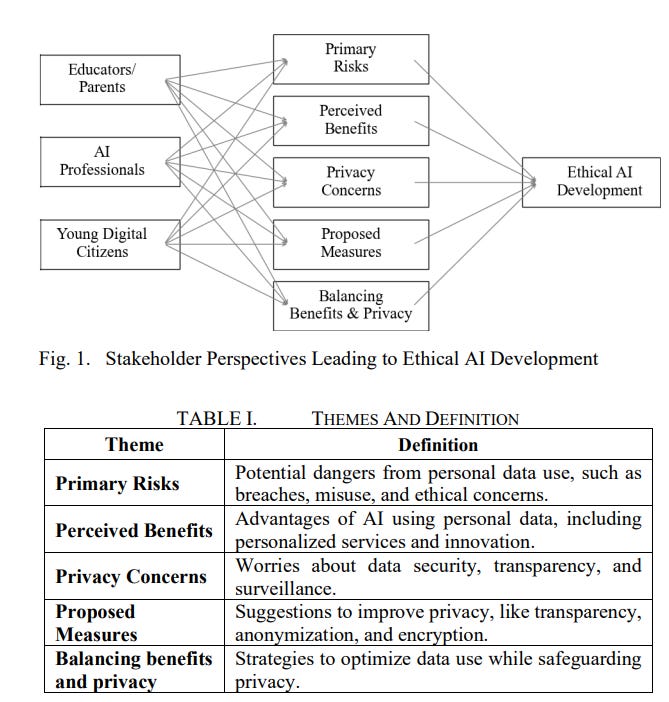
Study Highlights Stakeholder Concerns on Privacy and Ethics in Artificial Intelligence
• A study from Vancouver Island University highlights escalating privacy and ethical accountability concerns as AI systems are increasingly integrated into various facets of daily life
• Researchers stress the importance of transparency, privacy-by-design, and ethical oversight, offering actionable insights for balancing AI benefits with robust privacy protections
• Key privacy risks identified include data breaches and ethical misuse, while benefits such as personalized services and enhanced efficiency are also recognized;
Governance in AI Creative Industries: Addressing Consent, Credit, and Compensation Issues
• A recent study by researchers at Max Planck Institute and the University of Oxford explores the career-based harms creative professionals face due to generative AI technology;
• The study highlights critical governance gaps in AI systems, focusing on the "3 Cs" framework: consent, credit, and compensation for creators whose work trains AI models;
• Findings from interviews with creative workers underline the need for ethical AI training practices and propose recommendations for fairer AI governance in creative industries.
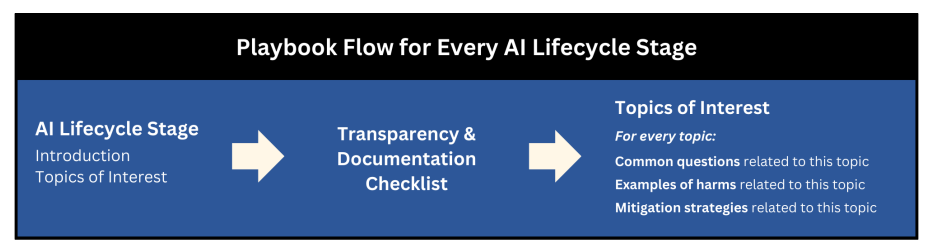
Generative AI Ethics Playbook Offers Strategies for Mitigating Machine Learning Risks
• The Generative AI Ethics Playbook offers strategies to identify and mitigate risks in machine learning systems, focusing on natural language processing, computer vision, and generative AI domains
• Designed for AI practitioners, the playbook includes documentation checklists, case studies, and harm mitigation resources for all stages of the AI lifecycle, from problem formulation to model monitoring
• Created through collaboration with 18 interdisciplinary experts, this playbook draws from over 100 resources, aiming to provide a comprehensive yet high-level resource for responsible AI deployment.
Governing AI Agents: Navigating Legal Challenges and Building New Frameworks
• The rapid evolution in AI is shifting from content-generating tools to autonomous agents capable of complex online tasks with minimal human oversight
• Challenges in AI governance are being addressed by applying economic theory and agency law to tackle issues like information asymmetry and discretionary authority
• Sustainable regulation of AI agents necessitates new frameworks encompassing inclusivity, visibility, and liability to adapt to their speed and decision-making complexities;
About SoRAI: The School of Responsible AI (SoRAI) is a pioneering edtech platform advancing Responsible AI (RAI) literacy through affordable, practical training. Its flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.